Lithium Deposits in the United States: A Comprehensive Analysis
Lithium, often referred to as “white gold,” is a critical resource in the global shift towards renewable energy. As a vital component of rechargeable batteries used in electric vehicles (EVs), smartphones, and renewable energy storage systems, lithium has garnered immense attention. With increasing demand for sustainable energy sources, securing lithium supplies has become a top priority for countries worldwide. In this blog post, we will explore the lithium deposits in the United States, delving into their significance, locations, challenges, and future prospects.
Understanding the Importance of Lithium
What is Lithium?
Lithium is a soft, silvery-white metal that belongs to the alkali metal group. It is highly reactive and has numerous applications across various industries, but its most significant use in modern times is in lithium-ion batteries. These batteries power everything from smartphones to electric vehicles, and they are essential for storing renewable energy produced by solar panels and wind turbines.
As the global economy continues to shift towards clean energy solutions, the demand for lithium has skyrocketed. According to industry reports, the demand for lithium is expected to increase by 500% by 2050, largely due to the rapid expansion of electric vehicles and renewable energy systems.
The Role of Lithium in Renewable Energy
Lithium plays a crucial role in the production of rechargeable batteries, specifically lithium-ion batteries, which are known for their high energy density and long life cycle. These batteries are essential for the mass adoption of electric vehicles and are used to store energy produced by renewable sources like solar and wind. As governments around the world implement aggressive climate policies to reduce carbon emissions, the demand for lithium has surged.
The United States, in particular, is facing the challenge of securing enough lithium to support its own clean energy goals. As of 2023, the U.S. relies heavily on lithium imports, making domestic production a critical factor in reducing dependence on foreign sources.
Lithium Deposits in the United States: Where Are They Found?
Overview of U.S. Lithium Deposits
While the United States has substantial lithium resources, they remain largely untapped. The country is home to several significant lithium deposits, which are crucial for bolstering domestic supply chains and reducing dependence on imports from countries like Australia and Chile.
The U.S. has two main types of lithium deposits:
- Lithium Brine Deposits: Found in salt flats and dry lake beds, lithium brine is extracted through evaporation.
- Hard Rock Lithium Deposits: Found in spodumene-bearing pegmatite rocks.
Below, we’ll explore the most notable lithium deposits in the United States.
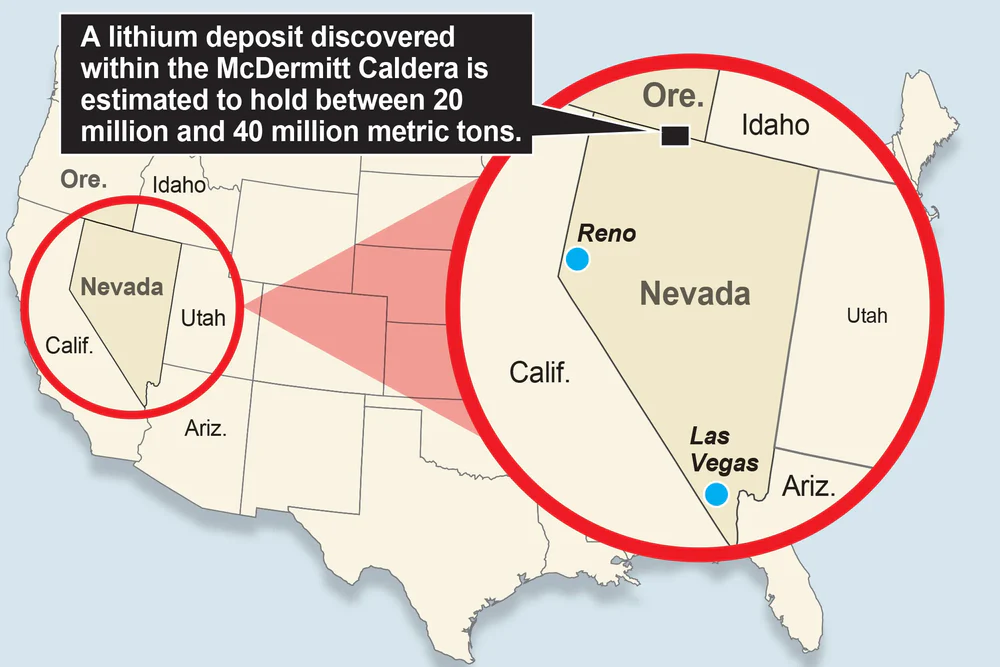
1. Thacker Pass, Nevada
Thacker Pass in Humboldt County, Nevada, is the largest known lithium deposit in the United States and one of the largest globally. This deposit, part of the McDermitt Caldera, is primarily a lithium claystone deposit, which is considered a relatively new and unconventional source of lithium.
Thacker Pass is owned by Lithium Americas Corp., and the company estimates that the deposit contains approximately 3.79 million tons of lithium carbonate equivalent (LCE). This project is expected to be a major source of lithium for decades to come, playing a pivotal role in securing the U.S. domestic lithium supply.
2. Silver Peak, Nevada
Located in Esmeralda County, Silver Peak is currently the only operating lithium mine in the United States. It is a lithium brine extraction facility that has been operational since the 1960s. Owned by Albemarle Corporation, Silver Peak uses an evaporation process to extract lithium from brine.
Though Silver Peak is a modest operation compared to some of the larger lithium producers globally, its historical significance and ongoing production make it an essential part of the U.S. lithium supply chain.
3. Kings Valley, Nevada
Kings Valley, also located in Nevada, is another promising lithium deposit. The project is owned by Livent Corporation and is still in the exploration phase. Early assessments suggest that Kings Valley contains substantial lithium resources, which could contribute to the growing demand for lithium in the U.S.
4. Clayton Valley, Nevada
Clayton Valley is an area that has gained significant attention due to its lithium-rich brine deposits. Several mining companies, including Pure Energy Minerals, are exploring opportunities in the valley. Although commercial-scale production has not yet begun, the potential for future development is high.
5. The Salton Sea, California
The Salton Sea region in California is one of the most promising locations for lithium extraction through geothermal brine. The geothermal plants in the area already produce electricity, and the possibility of extracting lithium from the geothermal brine has sparked interest from several companies, including Controlled Thermal Resources.
The unique feature of the Salton Sea deposit is its potential for environmentally friendly lithium extraction, as it relies on geothermal energy rather than traditional mining methods. If successful, this project could provide a significant portion of the U.S. lithium supply with a lower environmental footprint.
Challenges Facing Lithium Mining in the U.S.
Environmental Concerns
While lithium is crucial for renewable energy, its extraction process poses environmental challenges. Traditional lithium extraction methods, such as those used in lithium brine and hard rock mining, can result in water depletion, habitat destruction, and soil contamination. In the arid regions of Nevada, where many U.S. lithium deposits are located, water scarcity is a significant concern.
Lithium extraction from brine requires large amounts of water to evaporate, which can lead to the depletion of local water sources. This has raised concerns from environmental groups and indigenous communities who rely on these water supplies.
Regulatory and Legal Hurdles
Lithium mining in the U.S. is subject to various federal and state regulations. Environmental impact assessments, land use rights, and permitting processes can delay or even halt projects. The Thacker Pass project, for example, has faced opposition from local tribes and environmental activists who are concerned about the potential destruction of sacred land and the impact on wildlife.
In California’s Salton Sea region, efforts to ramp up lithium extraction are also facing regulatory challenges. The area is heavily regulated due to its environmental significance, and any extraction activity must comply with stringent environmental laws.
Economic Viability
Although the U.S. has abundant lithium resources, economic viability remains a challenge. Lithium extraction, particularly from unconventional sources like clay deposits or geothermal brine, can be expensive and complex. These factors have limited the development of new lithium projects in the U.S., despite the rising demand for the metal.
Furthermore, the price of lithium is volatile, influenced by global demand, production capacity, and supply chain disruptions. Mining companies must navigate these uncertainties when investing in new extraction technologies and scaling up production.
Future Prospects for Lithium Mining in the United States
Government Initiatives and Investments
To reduce reliance on foreign lithium imports, the U.S. government has implemented several initiatives aimed at boosting domestic lithium production. In 2021, President Biden’s administration announced plans to invest in critical minerals mining, including lithium, as part of the broader strategy to transition to clean energy.
The Department of Energy has also launched funding programs to support research into more sustainable lithium extraction methods and to develop a robust domestic lithium supply chain. These initiatives are expected to accelerate the development of new lithium mining projects and expand the U.S.’s role in the global lithium market.
Innovations in Lithium Extraction
New technologies are being developed to make lithium extraction more efficient and environmentally friendly. One promising method is direct lithium extraction (DLE), which allows for lithium to be extracted from brine with a smaller environmental footprint than traditional methods. Companies like Standard Lithium are exploring DLE technologies, which could be applied to projects like the Salton Sea.
In Nevada, efforts to extract lithium from claystone are also advancing. If these technologies prove to be commercially viable, they could unlock vast new sources of lithium in the U.S.
Lithium Supply and the Future of Electric Vehicles
The demand for electric vehicles (EVs) is a significant driver of lithium demand. As major automakers transition to electric models, the need for lithium batteries has become critical. Tesla, General Motors, and Ford are just a few of the companies ramping up EV production, creating an urgent need for reliable lithium supplies.
The U.S. must secure a steady lithium supply to support the growing EV industry and reduce dependence on imports. By investing in domestic lithium production, the country can position itself as a leader in the clean energy transition.
FAQs: Lithium Deposits in the United States
1. Where are the largest lithium deposits in the United States?
The largest lithium deposit in the U.S. is located in Thacker Pass, Nevada, which is one of the largest lithium reserves globally.
2. Is lithium mining environmentally friendly?
Traditional lithium mining can have environmental impacts, including water depletion and habitat destruction. However, new technologies, such as direct lithium extraction, aim to reduce these effects.
3. Why is lithium important for renewable energy?
Lithium is a key component in lithium-ion batteries, which power electric vehicles and store renewable energy, making it crucial for the clean energy transition.